With the increasing demand for intelligent driving systems and in-vehicle entertainment systems of new energy vehicles and the increasingly high integration and thinning of products, the transmission rate of the corresponding in-vehicle signal connection cables has also increased year by year. The traditional electronic wire-based LVDS signal line, has been unable to meet the requirements. The emergence of ultra-fine coaxial (MCC/SGC) has solved this difficulty very well; ultra-fine coaxial has many advantages such as small size, long life, good flexibility, stable impedance, and good shielding effect, while FAKRA Coaxial cable is a high-speed high-frequency cable that transmits radio frequency signals or high-definition camera signals based on ultra-thin coaxial (MCC/SGC) cables.
The FAKRA automotive connector is specially designed for automotive applications; the connector that meets the antenna standard is called the FAKRA connector, which uses the above micro-coaxial (MCC/SGC) cable and single-wire winding cable structure, and meets the requirements of the antenna standard. For FAKRA coaxial cable. Its typical structure is shown in the figure below, mainly including: FAKRA connector, FAKRA Inline connector, coaxial cable, PCB board end connector.
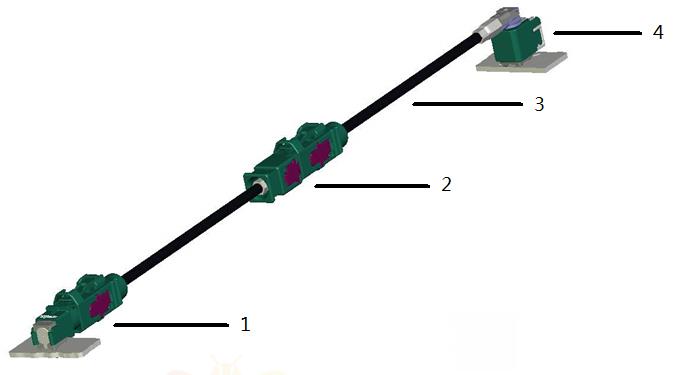
FAKRA coaxial cable connection structure diagram
Fakra Connector
The structure of the Fakra Connector:
Fakra connectors are generally used in automotive industry RF radio frequency signal connectors, GPS positioning systems, satellite radios, and vehicle Internet access. FAKRA automotive connectors are designed for automotive applications. They are based on the SMB connector interface FAKRA (Automated Expert Group) to establish a unified connector system and a standard that everyone will abide by. Thanks to its special standard locking system FAKRA connectors meet the high performance and safety requirements of today's automotive industry.
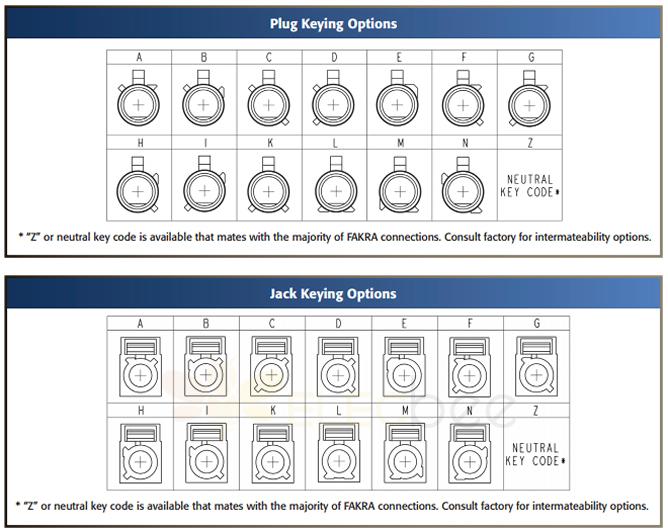
The structure of the FAKRA connector is divided into jack type or plug type, and the impedance specification is 50 ohms. The shape of FAKRA connector is divided into straight type or right angle type and free type. These FAKRA connectors are terminated with either crimp/solder or solder.
1. The overall structure of the board end and harness end connectors
A common Fakra connector consists of a plastic case, outer conductor, center conductor, insulator, crimp sleeve (harness end connector only) and secondary lock (harness end connector only).
2. Secondary lock, color + mechanical error proofing
Secondary Lock: Ensures the terminal is in place and increases terminal retention. Secondary locks are usually purple.
Color + mechanical error proofing: There is a structural design to prevent wrong mating on the mating interface of the connector, and different error proofing structures have corresponding plastic cases of different colors.
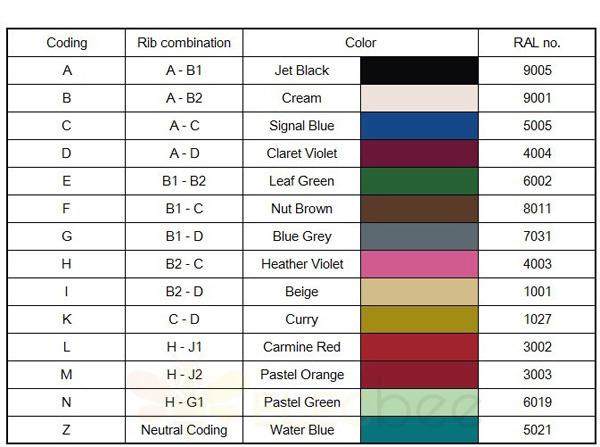
Basic introduction of FAKRA:
1. Performance parameters of Fakra connector
According to the parameter requirements in IS0 20860. Main electrical performance parameters: transmission frequency 0-4GHz; characteristic impedance 50 ohms; maximum carrying current 1A
Main mechanical performance parameters: lock retention force ≥ 100N error proof force ≥ 40N
2. Common applications
Wireless signal transmission: vehicle AM/FM; GPS; car networking (2~4GHz, including transmission), remote control, etc.
Video signal transmission application: Based on the outbreak of ADAS, it is mainly used in cameras.
3. Relevant standards
Design standard: ISO20860; USCAR18
Verification standard: LV214; USCAR2; USCAR17
Defines the main dimensions of FAKRA connectors in the axial and radial directions, including male and female connectors
4. Waterproof performance
Using the waterproof version of the harness end connector, the waterproof level of IPX7/IPX9K can be achieved at the mating interface of the connector.
FAKRA Coaxial Cable
From the anatomical structure diagram of the coaxial line, it can be seen that from the inside to the outside are: central wire, insulating layer, aluminum foil, braided shielding, and wire sheath. A coaxial cable is a compound composed of two conductors. The center wire of the coaxial cable is used to transmit signals. The metal shielding net plays two roles: one is to provide a current loop for the signal as a common ground wire for the signal, and the other is to provide a current loop for the signal. It is used as a shielding network for the signal to suppress the interference of electromagnetic noise on the signal. The central wire and the shielding net are interposed between the semi-foamed polypropylene insulating layer, which determines the transmission characteristics of the cable and effectively protects the middle wire.

As the name implies, the above concludes that the coaxial line is composed of a layer of insulating layer wrapped around the central copper conductor, and a metal mesh layer wrapped outside the insulating layer. Since the outer metal mesh and the central axis are on the same axis, So it is called coaxial line. The metal mesh can shield the electromagnetic interference of the outer layer. Part of the interference of the data line comes from the external magnetic field, and the other part comes from the magnetic field generated by itself when transmitting the changing signal. Due to the existence of the metal shielding network of the coaxial cable, the external magnetic field cannot pass through the shielding layer, and the internal magnetic field cannot pass through the shielding layer. When the signal is transmitted in the coaxial cable, the attenuation it receives is related to the transmission distance and the frequency of the signal itself. For high-frequency signals, the longer the transmission distance, the greater the signal attenuation. In order to achieve the purpose of long-distance transmission of high-frequency signals, a coaxial amplifier is usually used to amplify and compensate the signal.
FAKRA Board end connector
Compared with the wire-end connector, the FAKRA board-end connector has a difference in the structure of the interface. The more common difference is that there are two designs of the end surface of the outer conductor of the male end: insulator and air. After the two interfaces are mated with the female connector, there will be differences in performance. Another important factor affecting the performance of the male terminal board connector is the design of the connection with the PCB board at the tail of the connector. In order to achieve impedance matching, these factors will affect the transmission of signals: the distance between the root of the conductor in the board-end connector (close to the connector insulation medium) and the PCB board, the width of the signal line on the board, the working bandwidth of the PCB board, The size of the openings on both sides of the signal line on the board. When the operating frequency exceeds a certain threshold, both the board-side connector, PCB board, and the corresponding welding parameters must be fully demonstrated to avoid sudden changes in high-frequency signals in certain frequency bands.

Introduction to FAKRA Coaxial Signal Integrity
The signal integrity SI parameter usually refers to the distortion caused to the signal due to the characteristics of the path after the high-speed digital signal passes through the transmission path. The purpose of signal integrity analysis is to use the minimum cost and the fastest time to make the product meet the requirements of waveform integrity, timing integrity, and power integrity. Therefore, when choosing a FAKRA coaxial cable, you need to focus on the working bandwidth of the coaxial cable and the connector. In the entire link, the working bandwidth of each accessory will have an impact on signal transmission. For connectors of the same type and different manufacturers, it is necessary to refer to the product technical specifications to confirm the consistency of the selection and matching. In the actual application of vehicle cables, for the coaxial cable application in the bending area, considering the transmission loss and bending durability, a special bending-resistant cable with lower loss and larger diameter is usually used. For electrical appliances arranged in wet areas, special waterproof and dustproof FAKRA connectors are usually used. For arrangements in vibration areas, FAKRA connectors that meet vibration requirements also need to be considered. In short, FAKRA connectors and coaxial cables are accessories that have an important impact on the entire link transmission signal. By analyzing and mastering its main influencing factors, formulating corresponding design and testing measures to reduce and eliminate these influences is beneficial to the reliability and stability of high-frequency signal transmission.

Elecbee is a company specializing in the research and development, production and sales of electronic connectors, adapters and antennas. Whether it is technology, research and development, production or business, it is in the leading position in the industry. If you want to know more about our products or need related help and support, you can directly communicate with our technical staff in real time on the website or send an email to service@elecbee.com. All Elecbee staff look forward to cooperating with you.






